Software Rasterizer Lab
Note: click / save the images to view in high resolution
Background Knowledge
Lecture slides:
- from “Coordinate Spaces & Transformations” to “Alpha Blending and Intro to Geometry”, Nancy Pollard
[Link: http://15462.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2024/home]
More:
- Graphics Pipeline Summary, Wenxin Lai [Link]
Render Result
Features
Bresenham Line Algorithm
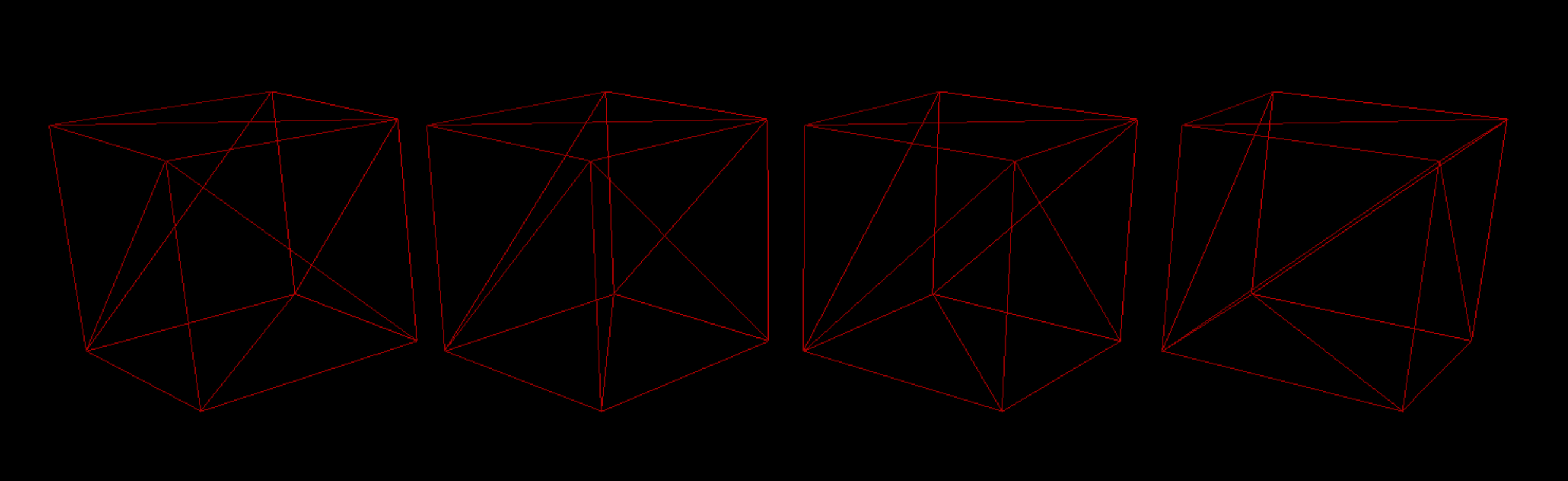 Cubes rendered in Wire Frame mode
Cubes rendered in Wire Frame mode
Depth Test
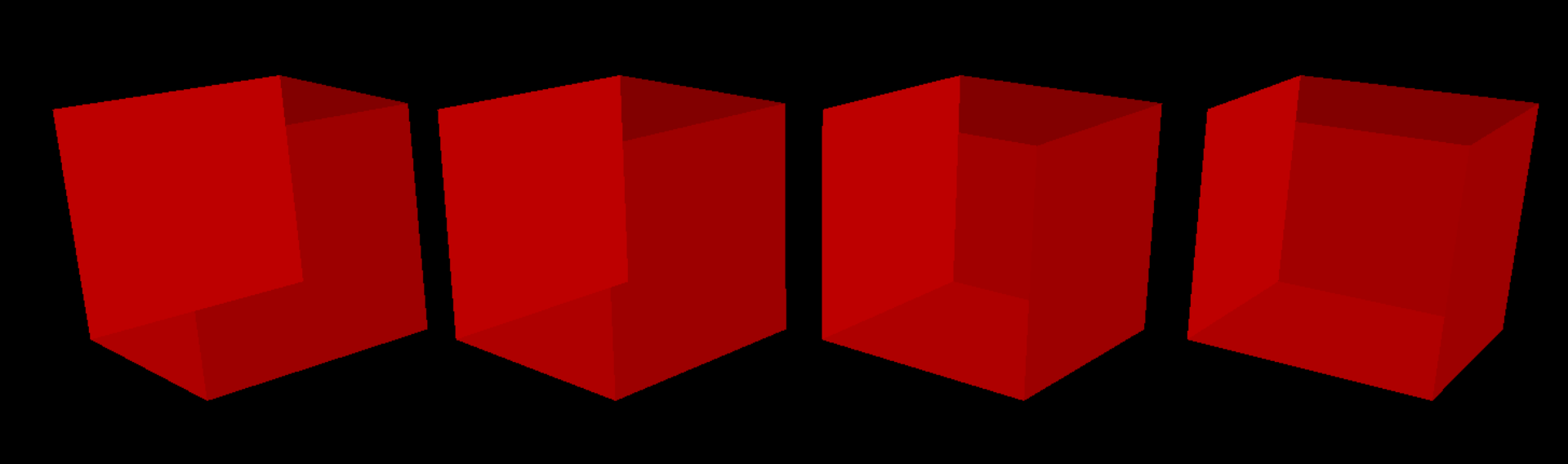 Before implementing Depth Support
Before implementing Depth Support
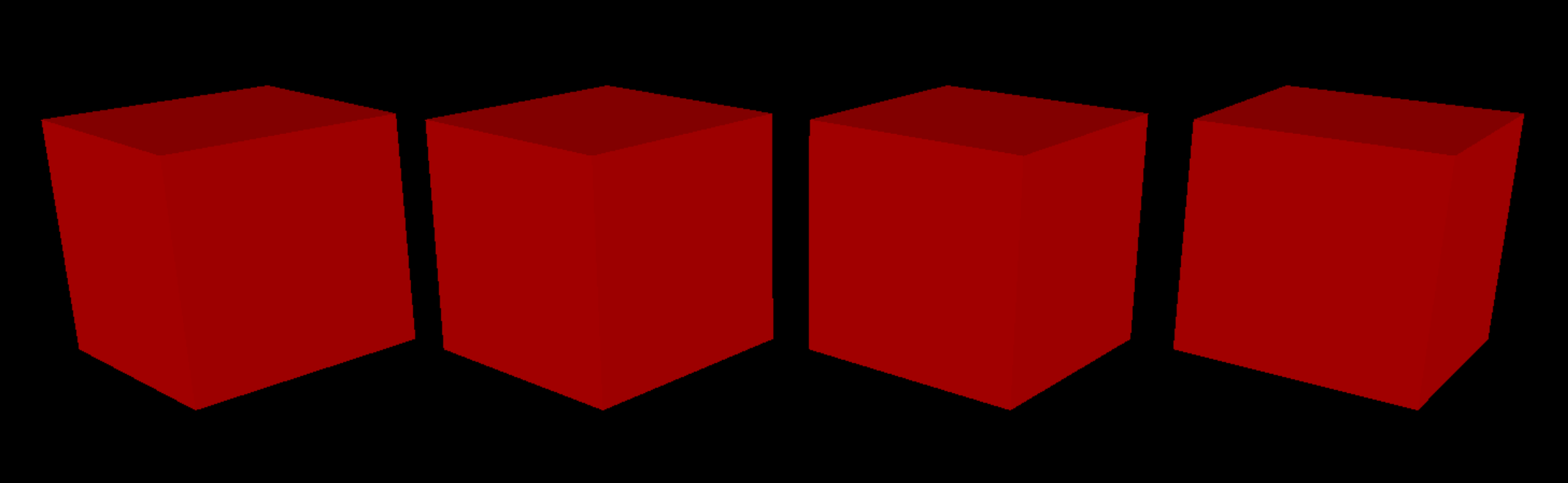 After implementing Depth Support
After implementing Depth Support
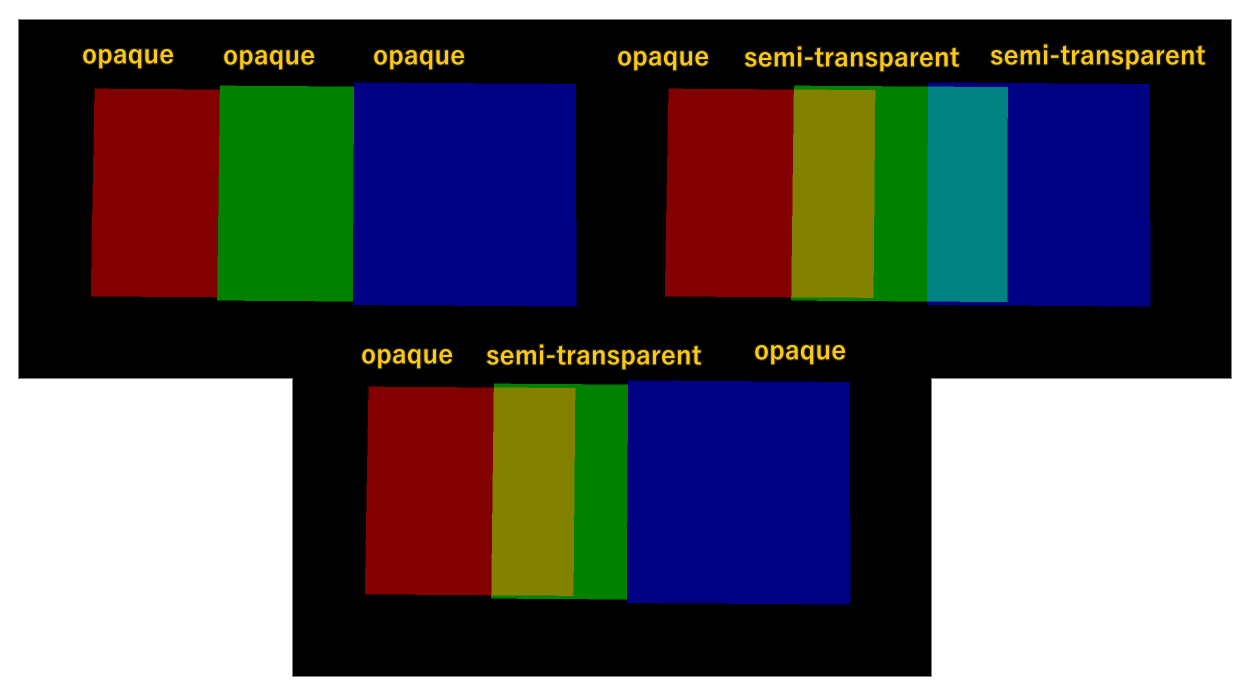
Alpha Blend
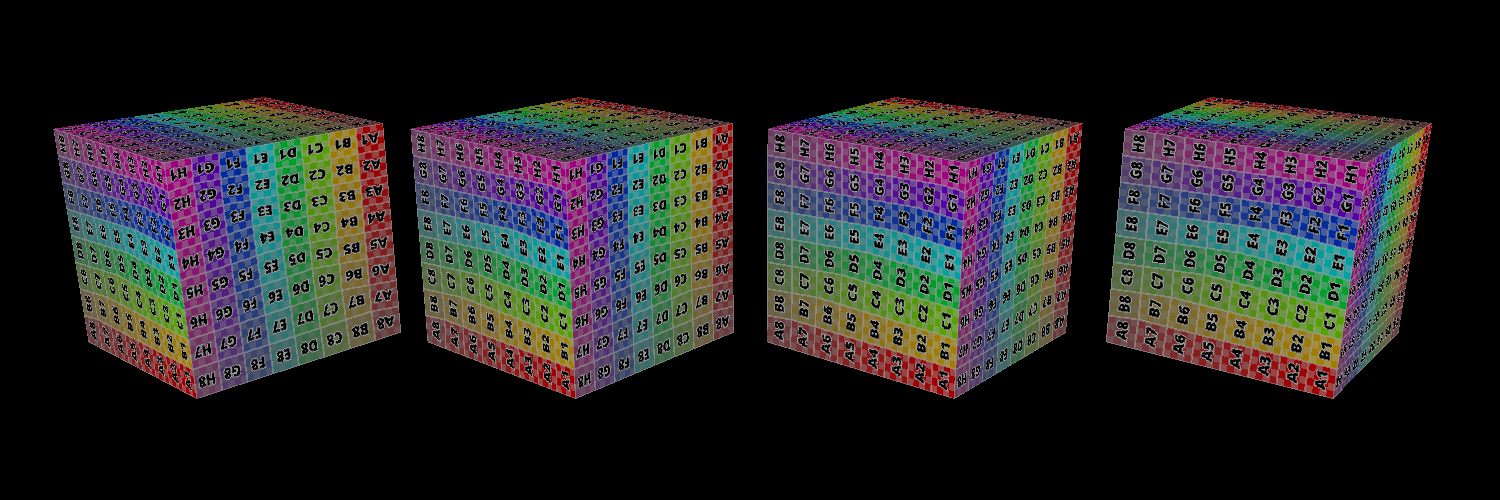
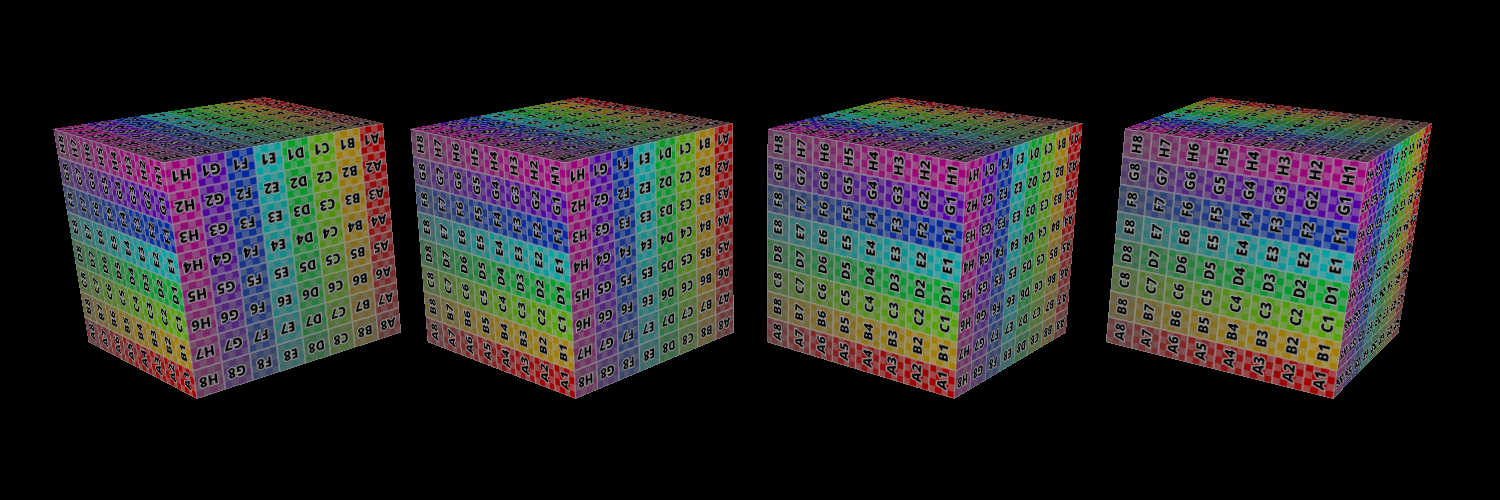
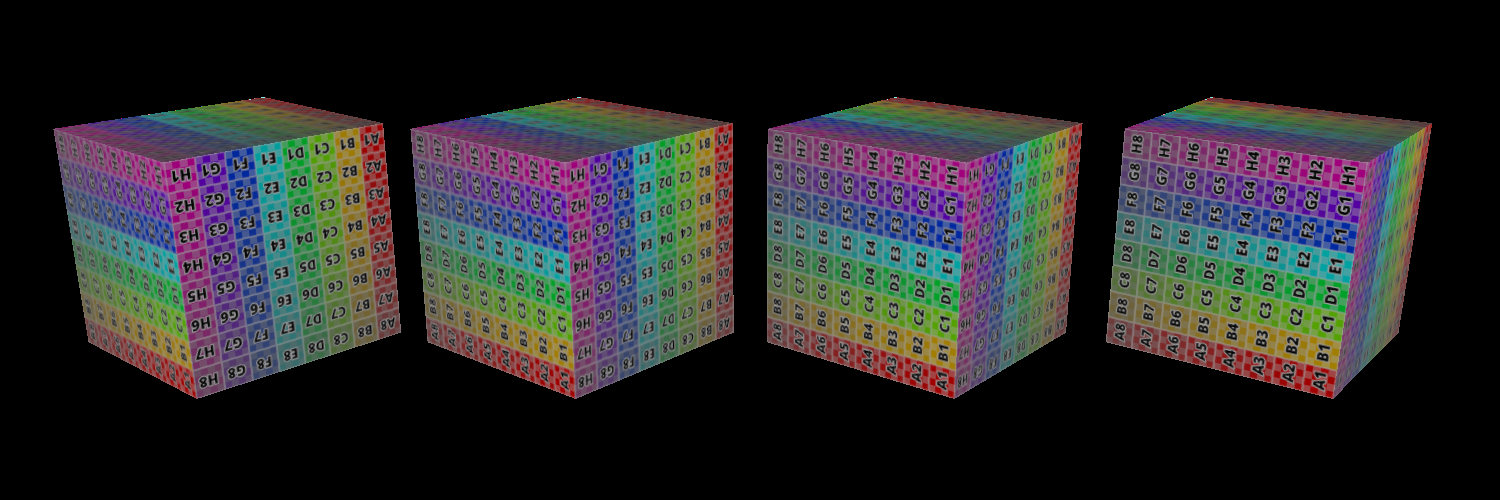
Replace Mode => Opaque Objects;
Add Mode => Semi-transparent Objects (with alpha 0.5);
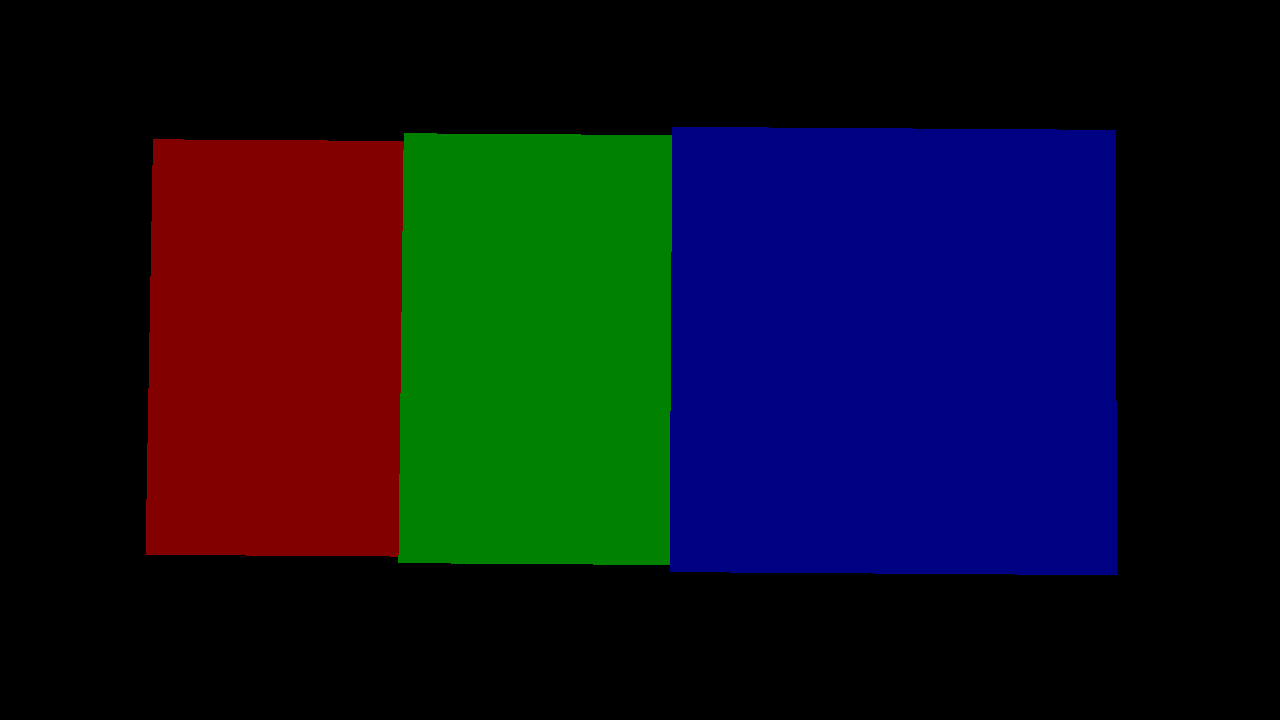 left: replace, middle: replace, right: replace
left: replace, middle: replace, right: replace
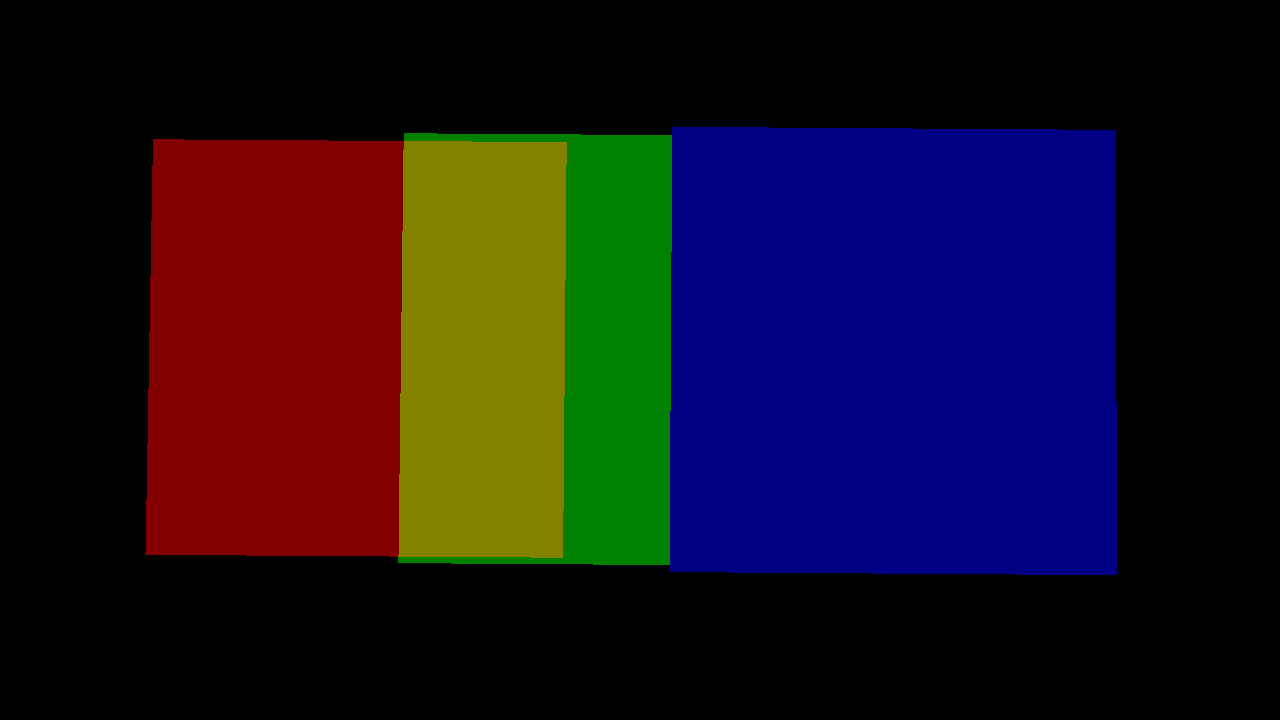 left: replace, middle: add, right: replace
left: replace, middle: add, right: replace
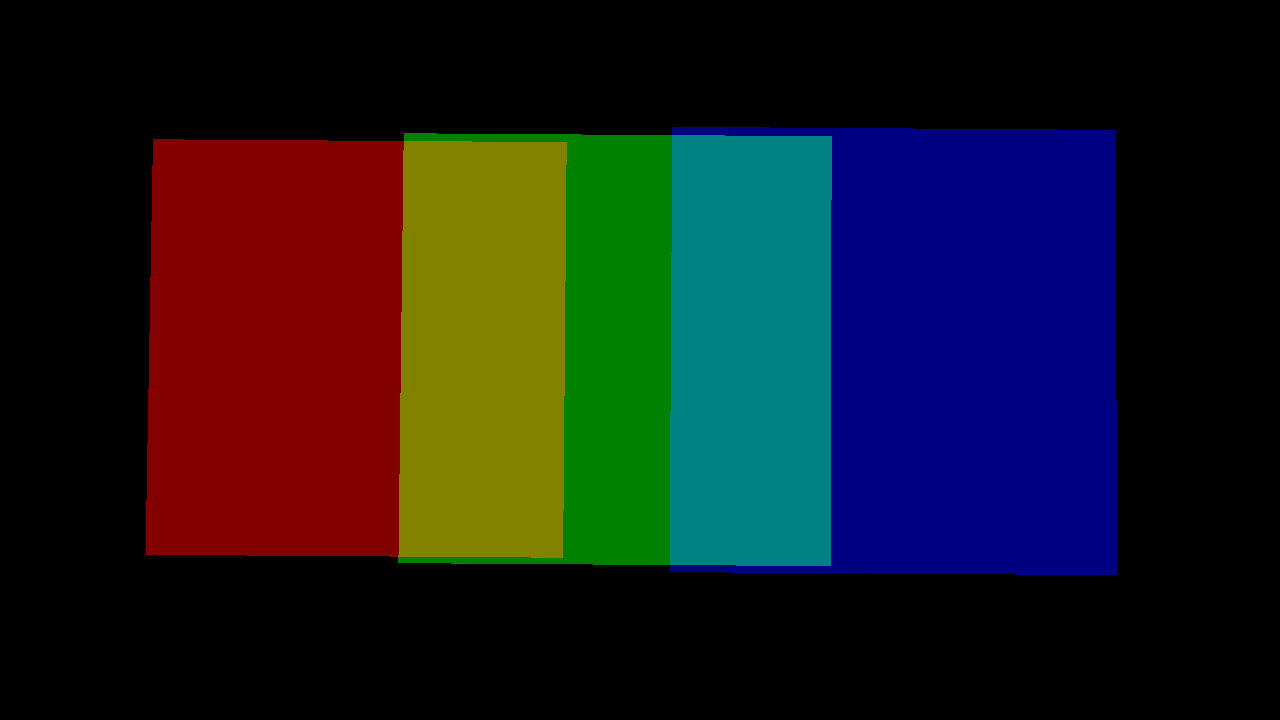 left: replace, middle: add, right: add
left: replace, middle: add, right: add
Display Mode (Vertex Interpolation Mode)
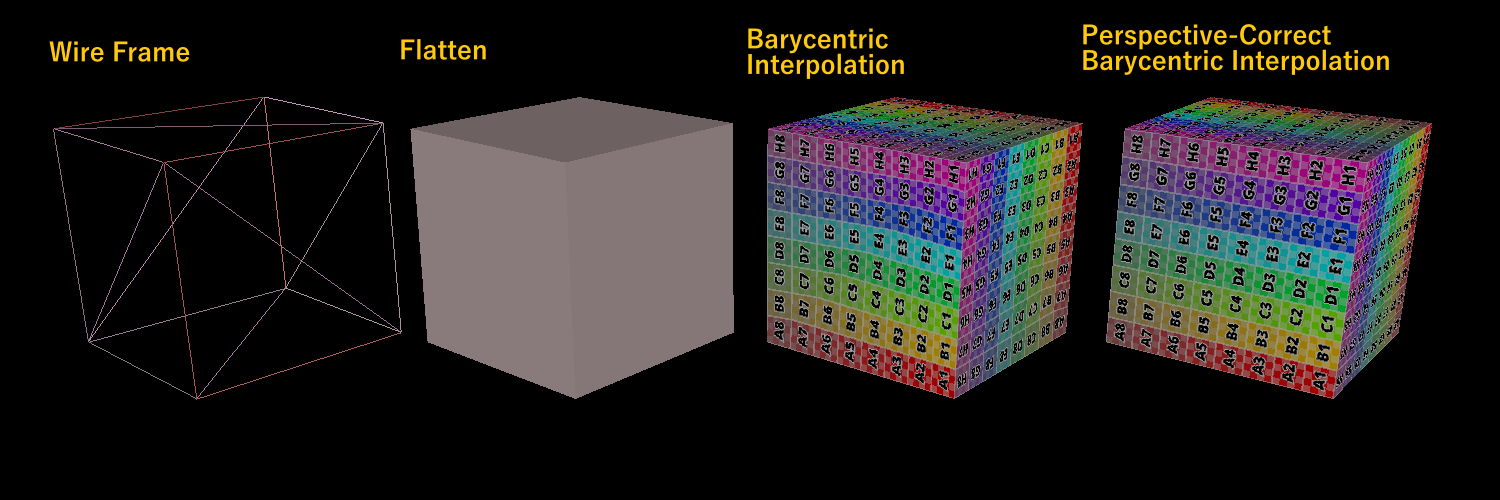
As shown in the figure above, in the barycenteric interpolation mode, the textures are distorted. It’s due to perspective projection. The barycentric interpolation of property values with depth is not affine. Therefore, the lines in 3D space projected onto the 2D screen may not be straight lines.
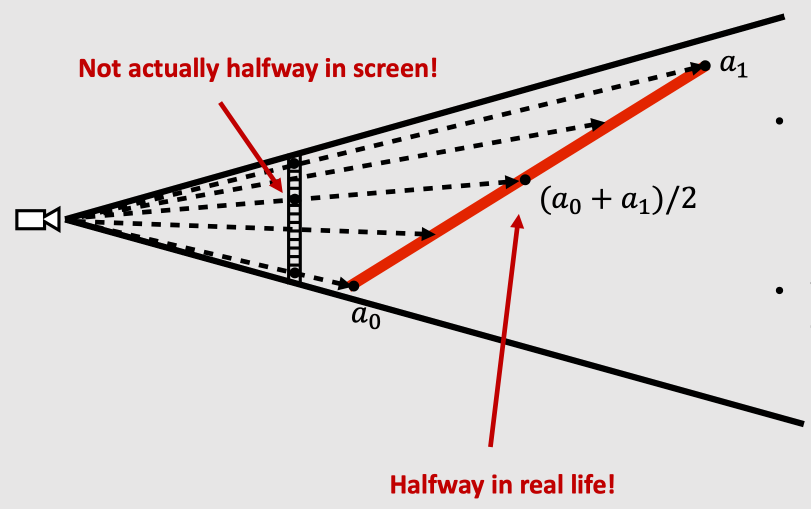 Barycentric Interpolation issue, img from http://15462.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2024/lecture/texture/slide_007
Barycentric Interpolation issue, img from http://15462.courses.cs.cmu.edu/spring2024/lecture/texture/slide_007
So, the perspective correct barycentric interpolation is implemented to fix this problem.
 Perspective-Correct Barycentric Interpolation
Perspective-Correct Barycentric Interpolation
Bilinear / Trilinear Interpolation Based on Mipmap
MXAA
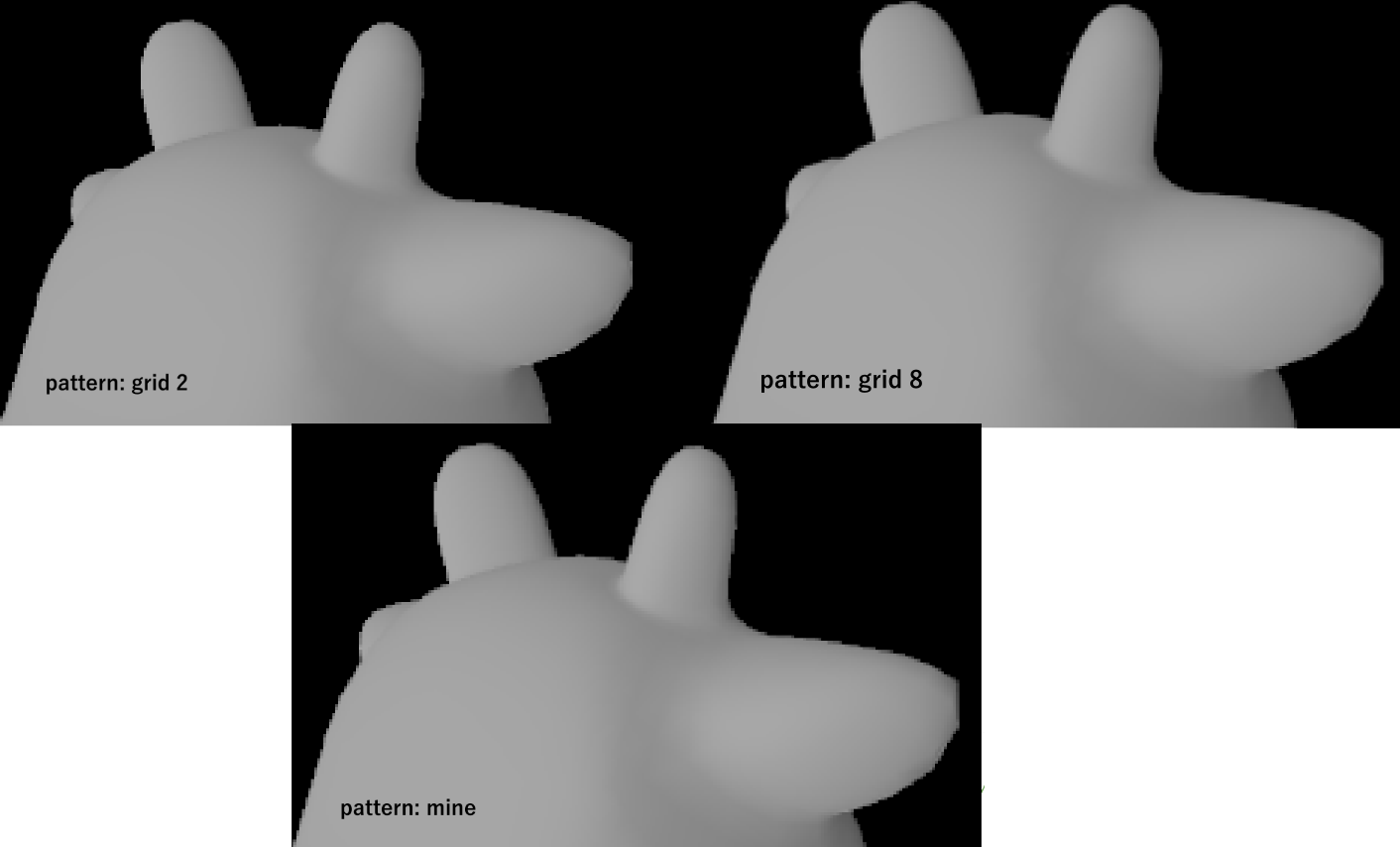
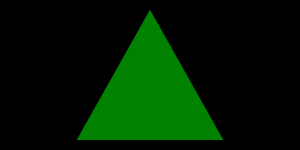 Render Result with MXAA (using Sample Pattern Grid 8*8)
Render Result with MXAA (using Sample Pattern Grid 8*8)
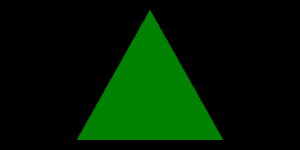 Render Result with MXAA (using Custom Sample Pattern with 5 sample points)
Render Result with MXAA (using Custom Sample Pattern with 5 sample points)
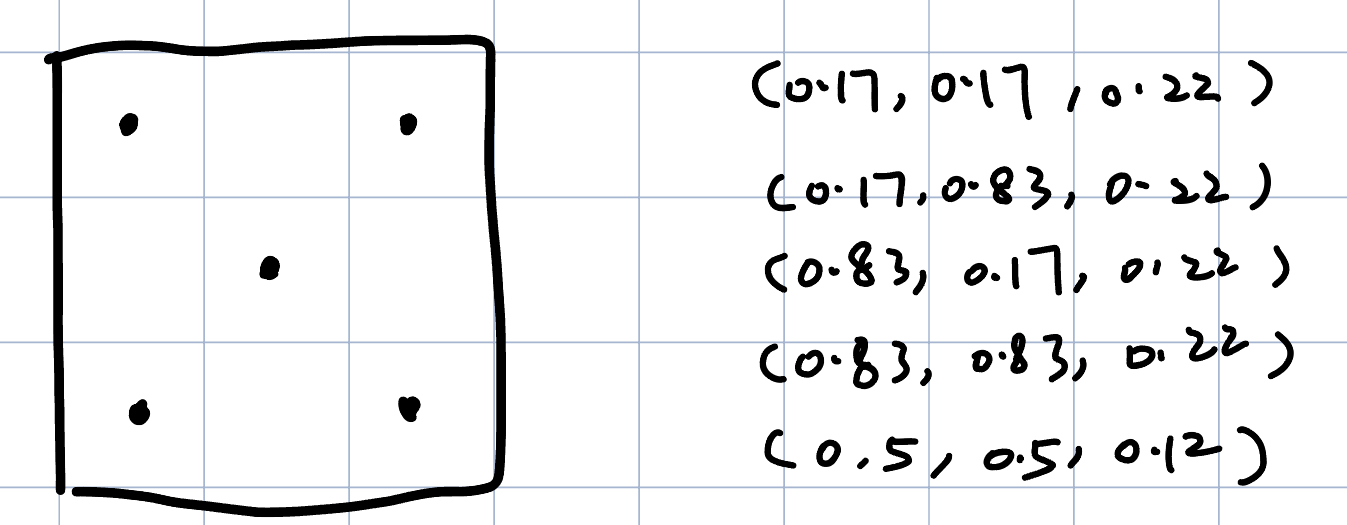 Custom Sample Pattern (x, y, weight)
Custom Sample Pattern (x, y, weight)
Features Comparision
 Comparision: different render modes
Comparision: different render modes
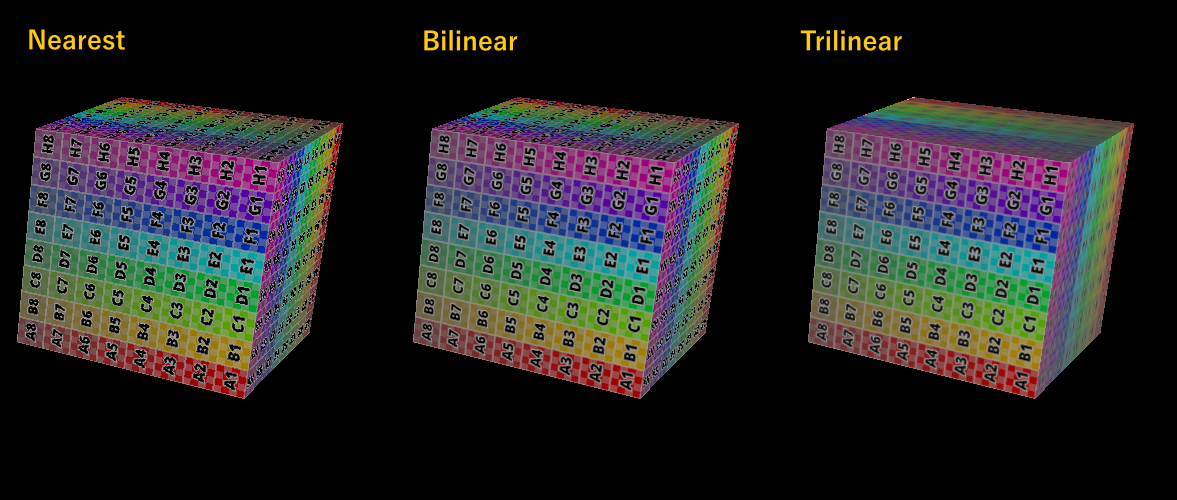 Comparision: different texture interpolation modes
Comparision: different texture interpolation modes
Classic Scenes
 Spot Cow Model Origin
Spot Cow Model Origin
 Bunny Model Origin
Bunny Model Origin
Acknowledgement
This project is based on the Scotty3D starter code, which is used in 15-462/662 (soon gonna be 15-362/662) Computer Graphics at Carnegie Mellon University.