Game Engine Architecture Glance
Why Layerd?
Decoupling and reducing complexity
Response for evolving demands
More flexible in higher layer and more stable in lower layer.
Rules
Normally only allow calls from upper layer to lower layer.
Layers (from high to low)
Tool Layer
Definition chain of editors built upon game engine, allow people to create games over the tools using flexible coding languages.
Very flexible, can choose C++ & Qt for best run-time efficiency and making UI; or C# & WPF to make powerful components; or Web & HTML for easy representation.
Different editors for different tools, very specialized, but remember to make them compatible with others if needed.
Function Layer
Definition including the parts like rendering, animation, physics, I/O Devices, AI which could make the game visible, movable and playable.
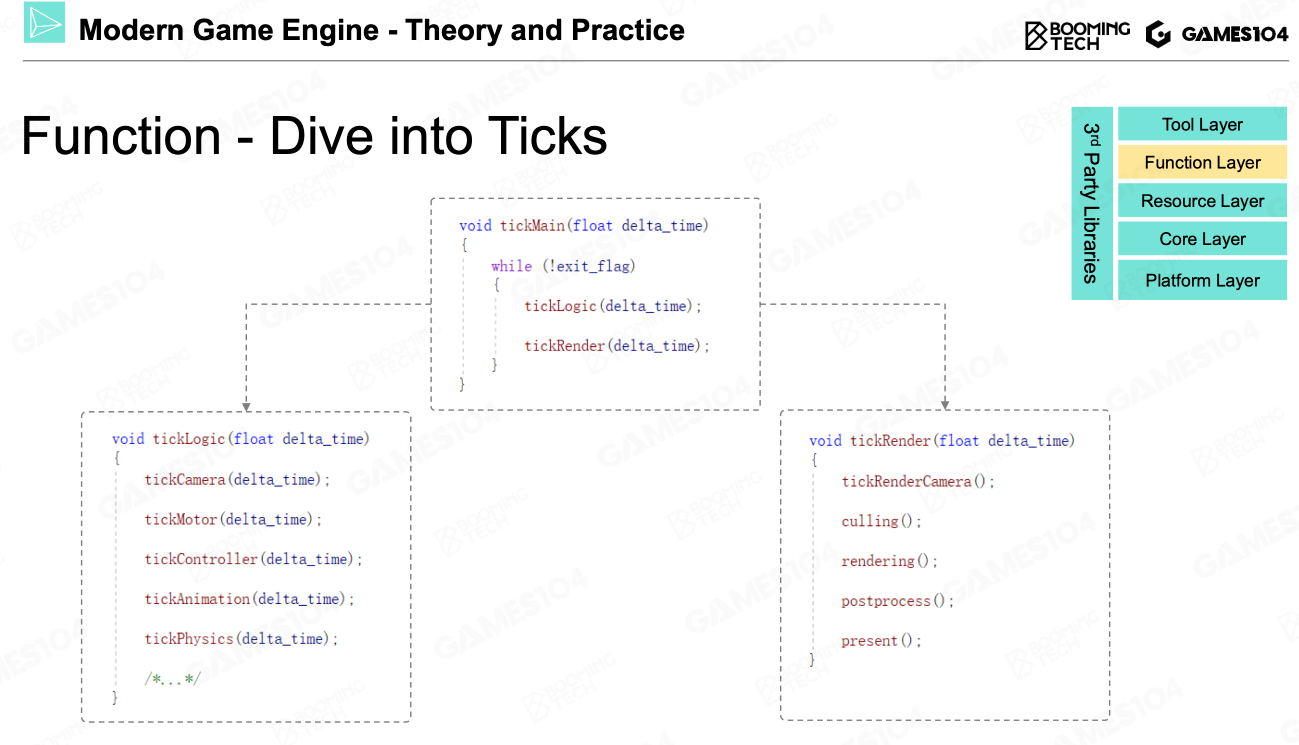
Clock: Make the World Alive
Tick based on which the displays needed to be updated
From Object-based Tick -> Component-based Tick
Object-based Tick: one game object updated then another;
Simple and Intuitive
Easy to debug
Component-based Tick: same components of diff objects updated simultaneously;
Parallelized processing
Reduced cache miss
Further more, in Component-based Tick, the parts needed to be updated are divided into LOGIC and RENDERING. (reason same as why gpu is used simultaneously with cpu: Graphic calculations are mostly vector operations, which is diff from normal operations in computers.)
When stepping into a new game engine, start from the CLOCK is recommended. We could find out how the system actually works here.
Events Mechanism
Decoupling event sending and handling
- Information transfer station
maintain message order, and the determinism property
Rendering
Refer to: https://livia23k.github.io/posts/games104-rendering/
Resource Layer
Definition everything about scene and level script and graph game logic data.
Resources
File format (.? -> .ast) remove all the redundancy data, transfrom it into a high efficiency data format asset (.ast) which will be used in the game engine.
Resource ID resource identity, which means a resource will be treated independently, and could be placed in different environment.
Everything is a game object in the game world.
Component-based coding
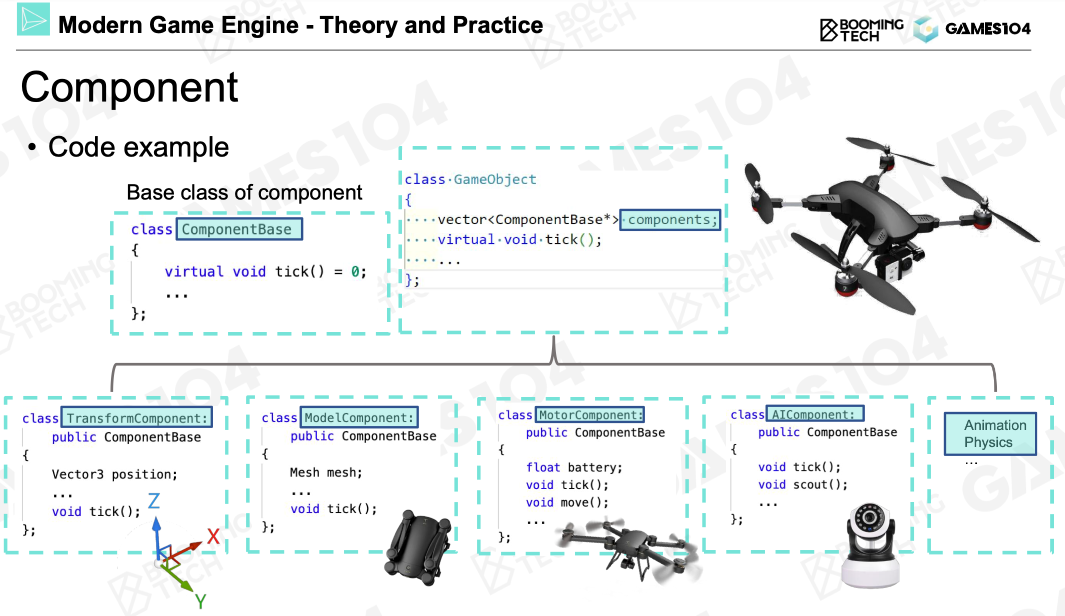 Example of Component Based Coding
Example of Component Based Coding
Resource Management
Runtime Asset Manager a virtual file system to load/unload assets by path reference, which could manage Asset lifespan and reference by handle system.
Resource life cycle management is an important problem in game engine. When players are in different game levels, the environment needs to be changed. If the resourses are not managed properly, then it will cause the system to crash. (due to huge amount of calculation caused by resource recycling …) Solution: real-time loading.
Scene Management for managing game objects in the sceme
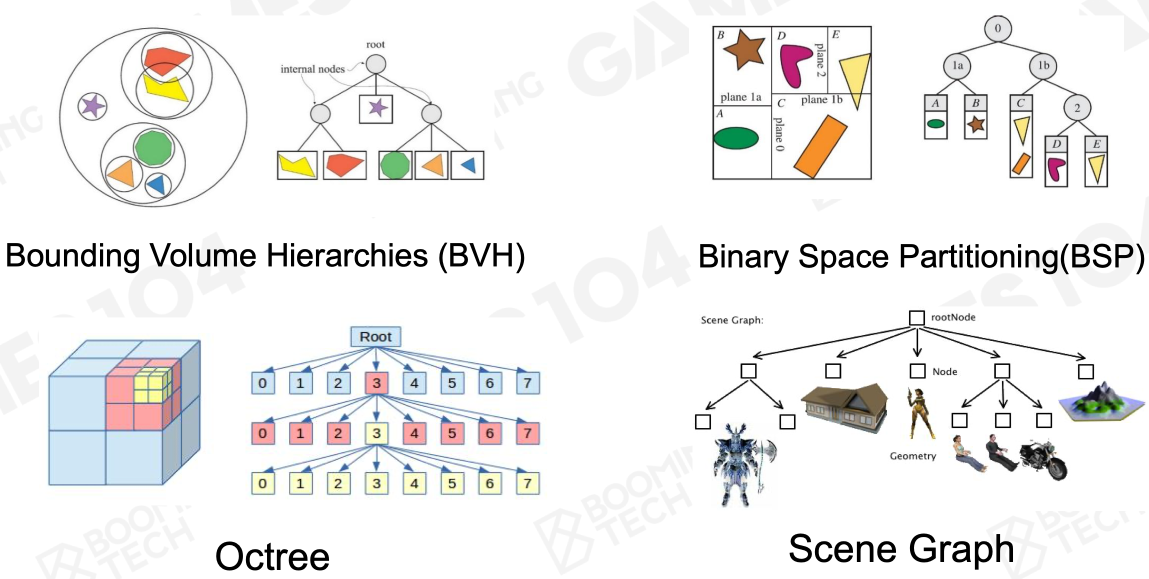
Spatial data structures:
Bounding Volume Hierarchies (BVH)
Binary Space Partitioning(BSP)
Octree
Scene Graph
Core Layer
High-efficiency math calculation E.g. SIMD, SSE (about high-efficiency vector operations).
Memory Management E.g. rewritten the implementation of containers in the engine, because C++ standard containers is more general, applying them will cause uncontrollable memory consumption which will leads to great fragmentation.
Platform Layer
Different platform has different Graphics APIs, and different hardware architecture.