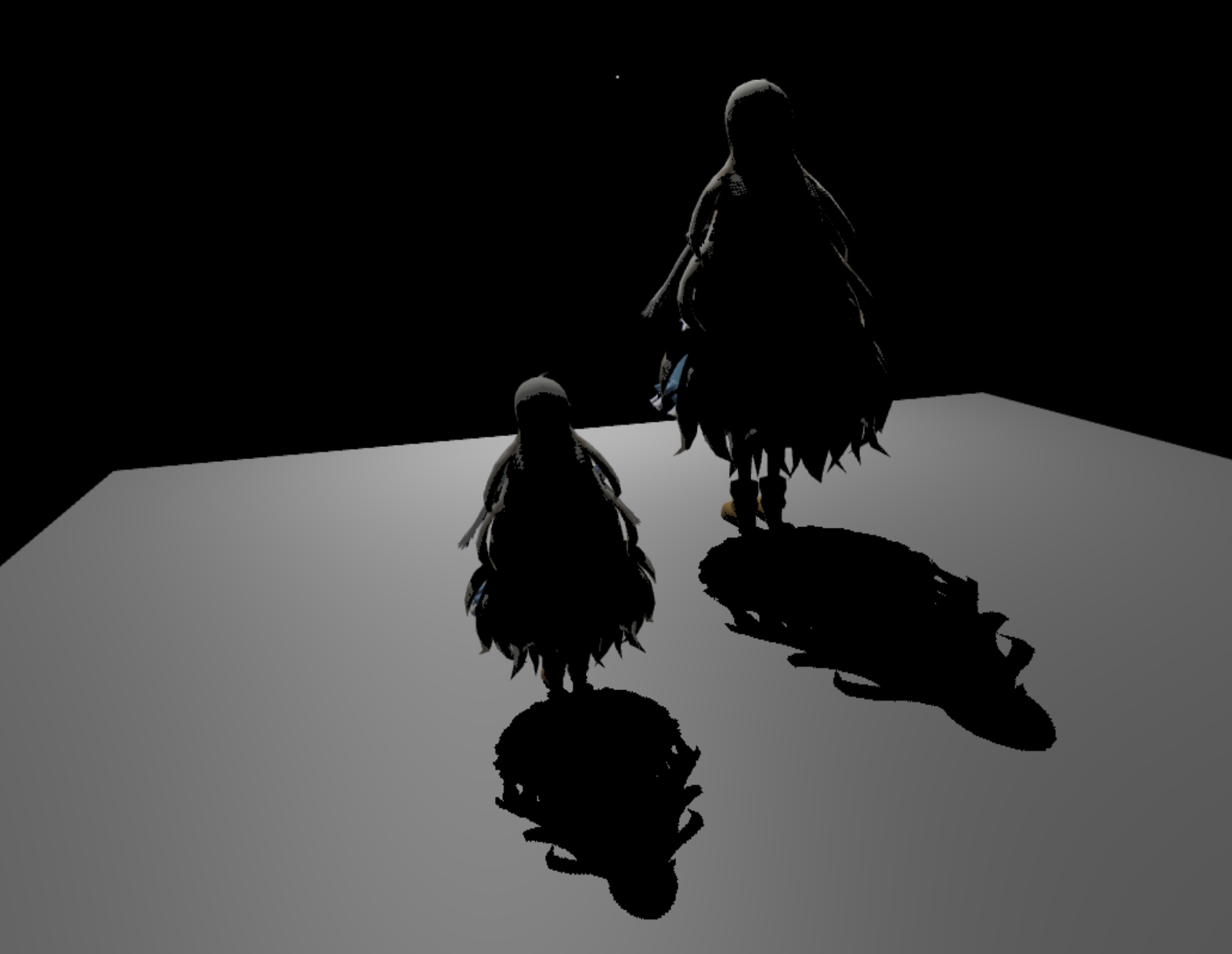
Shadow Lab (Shadow Map, PCF, PCSS)
Background Knowledges
Lecture slides:
- Real-Time Shadows 1 (Shadow Mapping, Percentage Closer Soft Shadows), Lingqi Yan [Link]
- Real-Time Shadows 2 (more about PCF & PCSS, Variance Soft Shadow Mapping, MIPMAP Moment Shadow Mapping), Lingqi Yan [Link]
- Real-Time Shadows 3 (Distance Filed Soft Shadows), Lingqi Yan [Link]
More info related:
图形学基础 - 阴影 - ShadowMap及其延伸, 杨鼎超 [Link]
自遮挡和漏光现象定义
Self-Occlussion Self-occlusion may result from floating-point calculation errors or occur when objects are two-sided and both sides occupy the same location. Therefore, a small bias is necessary to prevent the artifacts caused by this.
Light Leaks / Peter Panning Too much bias causes this problem, in which the object appears to float slightly above the underlying surface. —— p238, “Real Time Rendering (4th)”
Render Result
Shadowing Methods
Hard Shadow based on Shadow Mapping (SM)
Percentage-Closer Filtering (PCF)
Percentage-Cloer Soft Shadows (PCSS)
Comparison of Key Parameters
Note: All results are rendered in PCF mode.
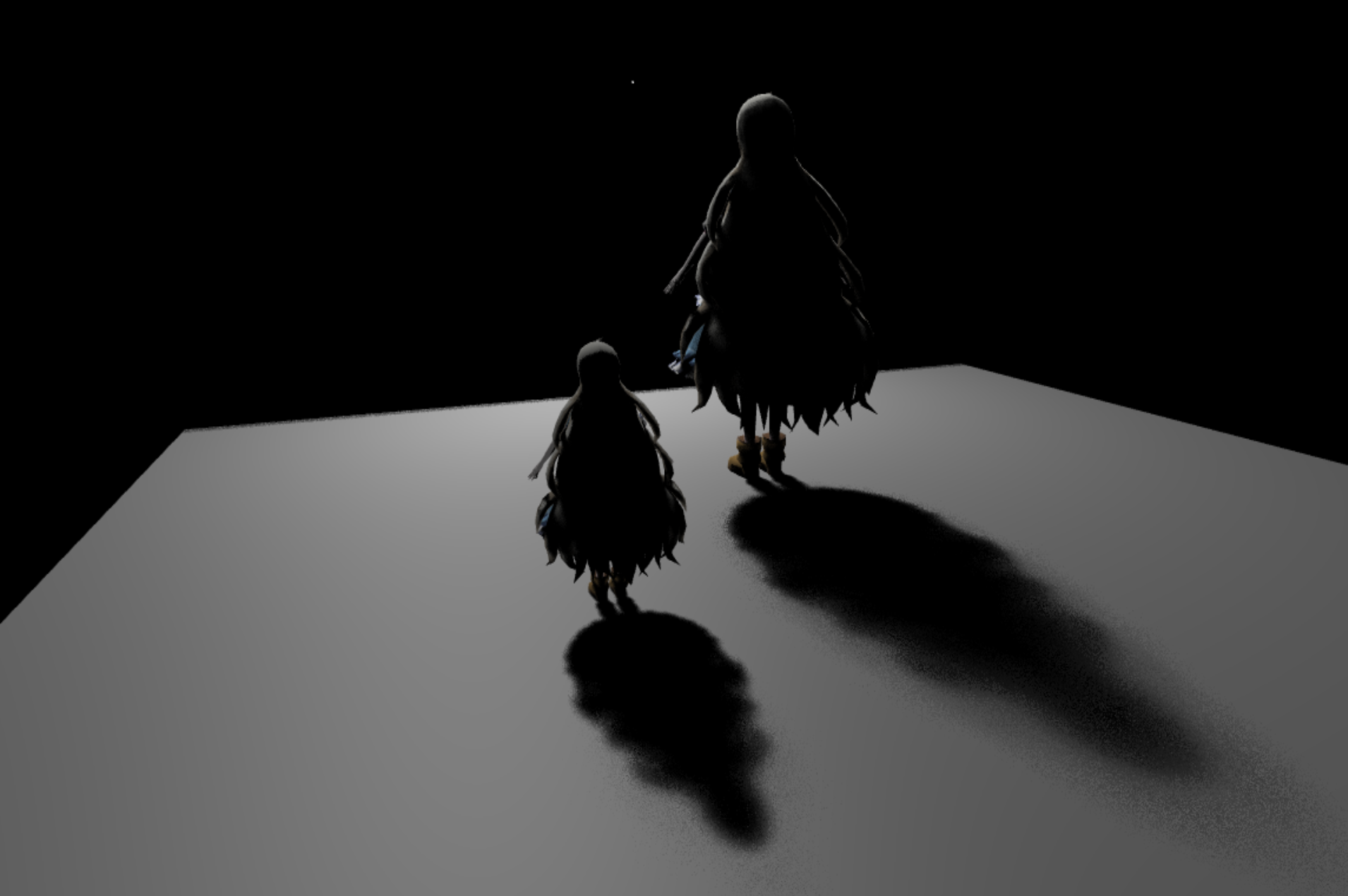
Sample Numbers
The quality of image increased as samples per pixel (SPP) increased, at the expense of the time needed for rendering.
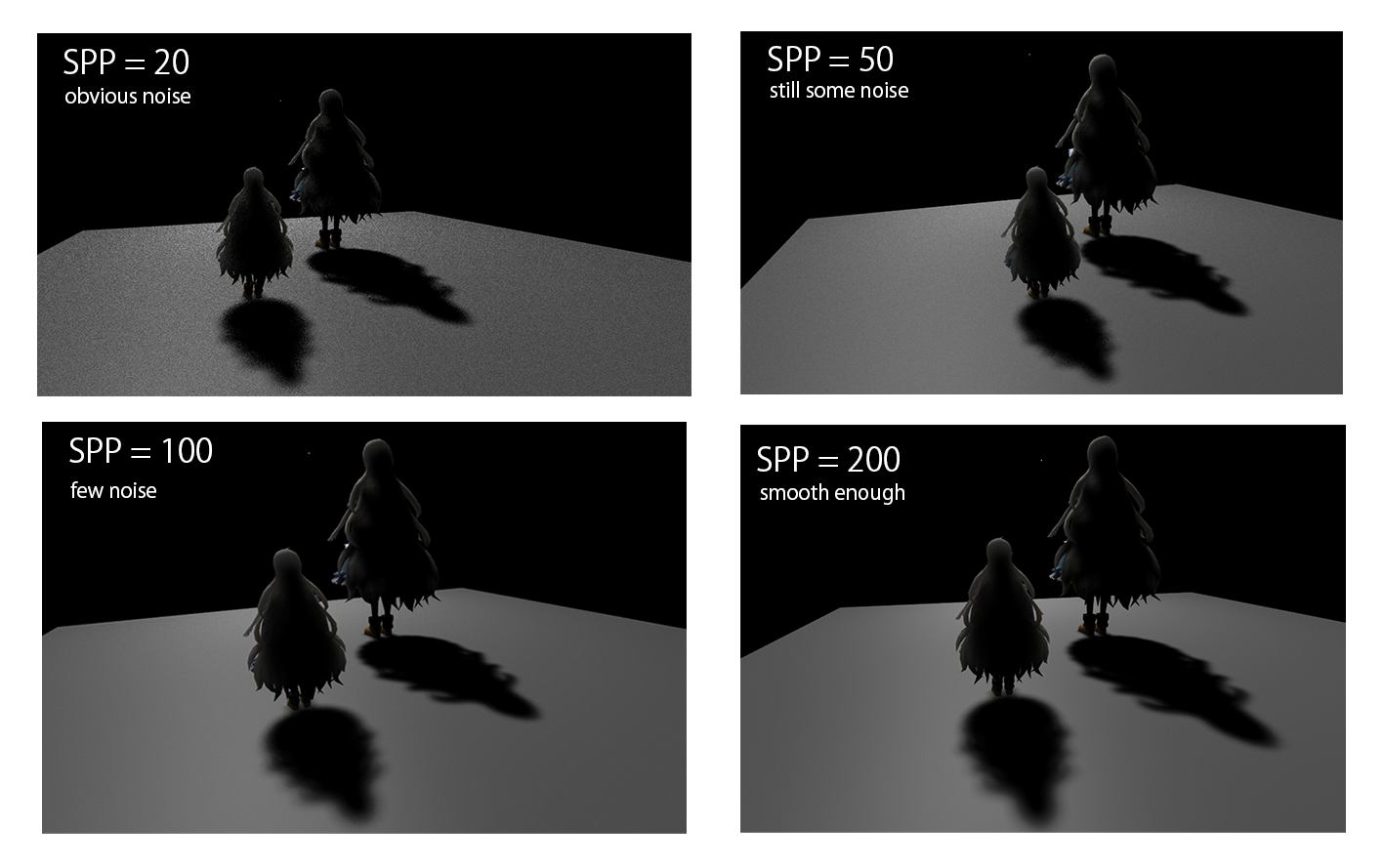 Comparison of different Sample Numbers
Comparison of different Sample Numbers
see [folder] for original pictures
Sampling Methods
In this lab, we are provided with 2 sampling methods, the Uniform Disk Sampling (as Figure 13.10 (b) shown) and Poission Disk Sampling. As SPP increased, Poission Disk Sampling yields nicer result.
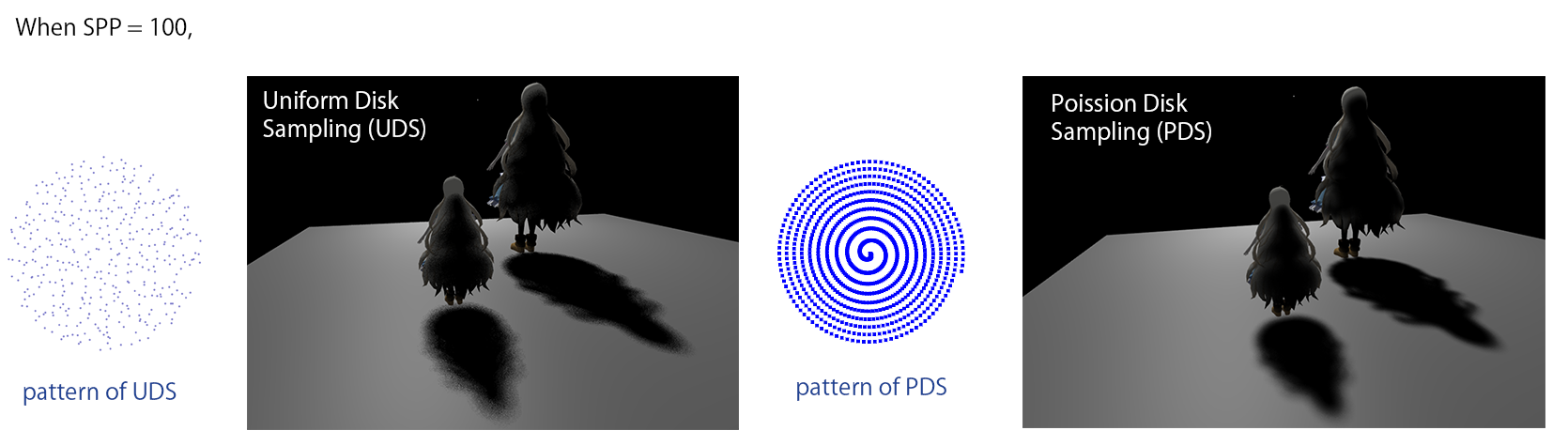 Comparison of different Sampling Methods, with 100 sample points
Comparison of different Sampling Methods, with 100 sample points
see [folder] for original pictures
Bias for Avoiding Self-Occlussion and Light Leaks
 Comparison of different Shadowing Bias
Comparison of different Shadowing Bias
see [folder] for original pictures
Acknowledgement
This project is based on the Soft Shadow starter code from GAMES202.